Enhancing Aviation Safety: Decoding The Safety Management System (SMS) For Aviation Professionals!

In the world of aviation, safety is of utmost importance(always, and always). With millions of passengers and tons of cargo being transported across the globe every day, maintaining a high level of safety is a top priority for airlines and aviation authorities alike. To achieve this, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) introduced the Safety Management System (SMS). So today, we have decided to try out best to decode and demystify the concept of SMS, its significance, and how it has transformed the aviation industry.
What is SMS in Aviation?(A Great Question!)
The Safety Management System (SMS) is a proactive and systematic approach to managing safety in aviation. It encompasses a set of policies, procedures, and practices designed to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with aviation operations.
The primary goal of SMS is to enhance safety by preventing accidents, incidents, and injuries. Unlike the traditional reactive safety practices, SMS focuses on risk management and continuous improvement to ensure safer skies.
Key Components of SMS
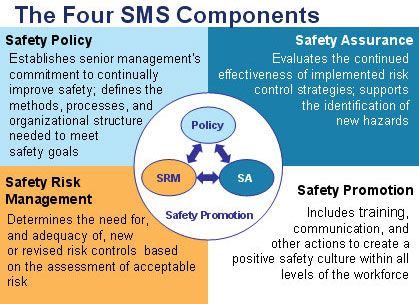
Safety Policy
The foundation of any SMS is a well-defined safety policy established by the organization's leadership. This policy outlines the commitment to safety, defines responsibilities, and sets safety objectives for the entire aviation operation.
Safety Risk Management
SMS involves identifying potential safety hazards, assessing their risks, and implementing measures to mitigate them. This proactive approach helps prevent accidents before they occur.
Safety Assurance
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of safety-related processes and procedures are vital for SMS. Safety assurance ensures that the implemented risk controls are effective and identifies areas that require improvement.
Safety Promotion
An essential aspect of SMS is promoting a safety culture within the organization. This involves training employees, raising awareness about safety issues, and encouraging reporting of safety-related events or concerns.
Implementation of SMS in Aviation

ICAO has mandated the implementation of SMS for all member states and aviation service providers. The process involves several steps, such as:
Gap Analysis
Organizations conduct an initial assessment to identify gaps in their existing safety processes and determine what changes are necessary to comply with SMS requirements.
Safety Policy Development
A clear and concise safety policy is drafted, demonstrating the organization's commitment to safety and its integration into the overall business strategy.
Risk Assessment
The organization identifies potential safety hazards and assesses the associated risks. Risk management processes are established to address these risks effectively.
Safety Performance Indicators (SPIs)
SPIs are established to measure the effectiveness of safety measures and to monitor safety trends and improvements over time.
Training and Education
Employees at all levels receive training on safety-related matters and are encouraged to actively participate in reporting safety concerns.
Safety is not just a destination; it's a continuous journey driven by Safety Management Systems (SMS)
Interfaces Between SRM and SA
In an aviation Safety Management System (SMS), Safety Risk Management (SRM) and Safety Assurance (SA) are two fundamental and interrelated processes. Both processes play distinct but complementary roles in ensuring the safety of aviation operations.
Safety Risk Management (SRM): SRM is the proactive process of identifying potential safety hazards, assessing the associated risks, and implementing measures to mitigate those risks. It involves conducting risk assessments, analyzing safety data, and making informed decisions to prevent accidents or incidents before they occur.
SRM helps aviation organizations to anticipate and address safety risks systematically, enhancing the overall safety performance.
Safety Assurance (SA): SA, on the other hand, is the process of verifying and monitoring the effectiveness of safety measures that have been implemented. It involves conducting safety audits, inspections, and performance evaluations to ensure that safety practices and procedures are being followed as intended.
SA aims to validate that the risk controls identified in the SRM process are functioning effectively and providing the desired safety outcomes.
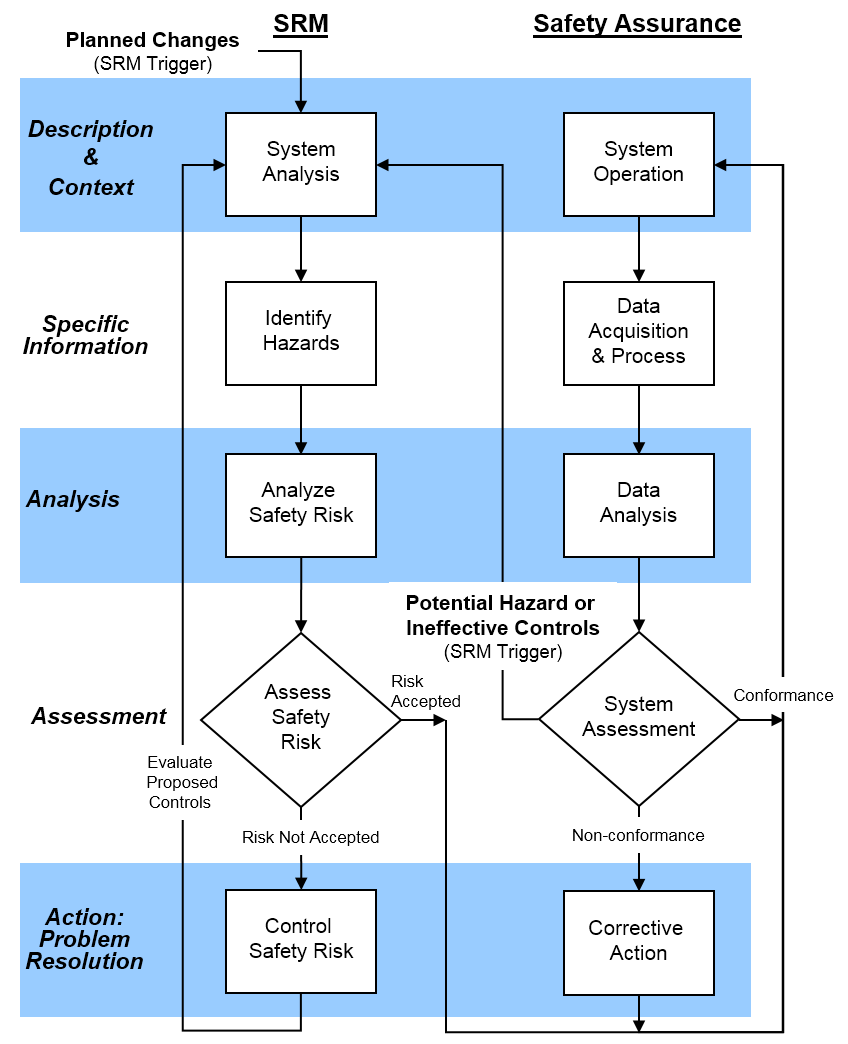
The flowchart depicting the interfaces between SRM and SA helps illustrate their interdependence and how they interact within the SMS. The interface attribute refers to the connections and relationships between the activities in the SRM and SA processes. Understanding these interfaces is crucial, especially when different departments or external entities are involved in the safety management process, such as maintenance, ground operations, or contracted services.
With SMS as our co-pilot, aviation is on a journey of continuous improvement, reaching new heights of safety
When evaluating these interfaces, several critical aspects need attention
a. Flow of Authority and Responsibility: It is essential to define clear lines of authority and responsibility for safety-related decisions and actions. Ensuring that responsibilities are well-defined helps avoid confusion and ensures a coordinated approach to safety management.
b. Communication: Effective communication is vital for the successful implementation of SMS. All stakeholders must be able to communicate safety-related information efficiently and transparently. This includes sharing safety data, reporting incidents, and disseminating safety-related changes or improvements.
c. Procedures and Documentation: Standardized procedures and documentation are integral to both SRM and SA. Consistent and well-documented processes aid in maintaining a robust safety management system, facilitating continuous improvement, and ensuring that safety practices are followed consistently.
d. Collaboration: SRM and SA often involve multiple stakeholders within an aviation organization. Cooperation and collaboration between different departments and teams are essential for effective risk management and safety assurance. This collaboration helps in sharing knowledge, experiences, and best practices, fostering a safety culture throughout the organization.
Clearly, the interface between Safety Risk Management and Safety Assurance is vital for the success of an SMS. Understanding and addressing the interactions between these processes allow aviation organizations to develop a comprehensive safety management approach, continuously improving safety practices, and ensuring the highest level of safety for passengers, crew, and all stakeholders involved in aviation operations.
Benefits of SMS in Aviation
The implementation of SMS in aviation has led to several significant benefits:
- Accident Prevention: By proactively identifying and addressing potential risks, SMS helps prevent accidents and incidents from occurring.
- Continuous Improvement: SMS promotes a culture of continuous improvement, leading to better safety performance and operational efficiency.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: SMS relies on data analysis to make informed decisions, enhancing the effectiveness of safety measures.
- Stakeholder Confidence: SMS implementation demonstrates a commitment to safety, enhancing the confidence of passengers, regulators, and stakeholders.
The Safety Management System (SMS) is a critical development in the aviation industry, transforming safety practices from reactive to proactive. By emphasizing risk management, continuous improvement, and a safety-oriented culture, SMS has significantly contributed to reducing accidents and incidents in aviation.
As it continues to evolve and be embraced globally, we can look forward to safer skies and more efficient aviation operations for years to come.
Importance of SMS for Pilots

For pilots, knowing and understanding the Safety Management System (SMS) is equally important for several reasons:
- Flight Safety: As the individuals responsible for operating the aircraft, pilots play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety of passengers, crew, and the aircraft itself. Understanding SMS enables pilots to be proactive in identifying potential safety hazards and taking appropriate actions to mitigate risks during flight operations.
- Decision Making: SMS training equips pilots with a systematic approach to decision-making, especially in complex and challenging situations. By considering safety risks and potential consequences, pilots can make well-informed decisions that prioritize the safety of the flight.
- Emergency Response: In case of emergencies or unexpected events during a flight, pilots must act swiftly and effectively. Knowledge of SMS principles helps them manage the situation, communicate with the cabin crew and air traffic control, and execute the appropriate emergency procedures.
- Reporting Safety Events: Pilots' understanding of SMS encourages them to actively report safety-related events, incidents, or near-misses. Timely and accurate reporting contributes to a comprehensive safety data collection system, which is crucial for analyzing trends and implementing safety improvements.
- Compliance with Regulations: Aviation authorities often require pilots to undergo SMS training as part of their regulatory requirements. Compliance with these regulations ensures that pilots and the airlines they work for maintain adherence to international safety standards.
- Safety Culture: SMS fosters a safety-oriented culture within aviation organizations. Pilots who are familiar with SMS principles are more likely to adopt safety-conscious behaviors, support safety initiatives, and contribute to creating a robust safety culture.
- Collaboration and Communication: SMS emphasizes the importance of open communication and collaboration among all stakeholders in the aviation industry. Pilots who understand SMS principles can effectively communicate safety concerns, share feedback, and actively engage in safety-related discussions with the airline's safety management team.
- Continuous Learning: Safety is a dynamic and ever-evolving aspect of aviation. Pilots who are knowledgeable about SMS are more likely to engage in continuous learning, keeping themselves updated on new safety practices and developments in the industry.
Remember, SMS is integral to ensuring the safety of aviation operations, and pilots play a crucial role in its implementation. By knowing and understanding SMS principles, pilots can make informed decisions, actively contribute to a safety-oriented culture, and be better prepared to handle various safety-related situations during flights.
Importance of SMS for Cabin Crew

It is essential for cabin crew to know and understand the Safety Management System (SMS) for several reasons:
- Passenger Safety: Cabin crew members are responsible for the safety and well-being of passengers on board. Understanding SMS enables them to identify potential safety hazards, report safety concerns, and take appropriate measures to ensure the safety of passengers during the flight.
- Emergency Response: In the event of an emergency, cabin crew must be well-prepared to handle the situation efficiently. SMS training equips them with the necessary knowledge to assess risks, make informed decisions, and respond effectively to emergencies, contributing to better outcomes and passenger protection.
- Risk Mitigation: SMS emphasizes proactive risk management. When cabin crew members are familiar with SMS principles, they can recognize potential risks early on and take steps to mitigate them before they escalate into safety incidents.
- Reporting and Communication: Effective communication is crucial in aviation. Understanding SMS helps cabin crew members to report safety-related incidents or concerns accurately and promptly. Proper reporting contributes to a robust safety data collection system, enabling the organization to analyze data and implement improvements.
- Safety Culture: SMS promotes a safety-oriented culture within an airline or aviation organization. Cabin crew members who understand and embrace SMS principles actively participate in safety-related initiatives, contributing to the overall safety culture of the organization.
- Compliance and Regulations: Many aviation authorities require airlines to have an SMS in place and ensure that their employees, including cabin crew, are trained in SMS implementation. Complying with these regulations ensures that airlines meet international safety standards and maintain their operating certifications.
- Continuous Improvement: SMS fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Cabin crew members who are knowledgeable about SMS can provide valuable feedback, identify areas for improvement, and contribute to the enhancement of safety procedures and practices within the airline.
Cabin crew play a critical role in ensuring the safety of passengers during flights. Understanding and implementing SMS principles empowers them to be proactive in managing safety risks, responding to emergencies, and actively contributing to a culture of safety within the aviation organization.
Some Must Know Case Studies

Here are a couple of real case studies that highlight the importance of Safety Management System (SMS) implementation in aviation:
Air France Flight 447 (2009)

On June 1, 2009, Air France Flight 447, an Airbus A330, crashed into the Atlantic Ocean during a flight from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, to Paris, France. The accident resulted in the loss of all 228 passengers and crew on board. The investigation revealed that the aircraft's pitot tubes, which are critical for providing airspeed data, became blocked by ice, leading to the autopilot disengaging.
One of the significant factors contributing to the accident was the lack of understanding of the aircraft's automated systems by the flight crew. Additionally, there were shortcomings in the airline's SMS, which failed to address training deficiencies and adequately prepare the pilots to handle such critical situations effectively.
The incident underscored the importance of robust SMS training, effective communication, and continuous improvement in aviation safety procedures.
More here
“The sky is not a place, it’s a feeling.”
Colgan Air Flight 3407 (2009)

On February 12, 2009, Colgan Air Flight 3407, a Bombardier Dash 8-Q400, crashed near Buffalo, New York, while on approach to the airport. The accident resulted in the loss of all 49 passengers and crew on board and one person on the ground. The investigation found that the pilots' improper response to the aircraft's stall warning system led to the loss of control.
The accident brought attention to the need for enhanced safety training and the implementation of SMS in regional airlines. The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) investigation revealed that the captain's inadequate training and performance, as well as the airline's deficient safety culture and fatigue management, were contributing factors. Proper SMS training could have helped identify and address these issues, preventing the tragedy.
More here
These case studies demonstrate how the absence of a robust SMS can have serious consequences for aviation safety. Implementing SMS with a focus on risk management, continuous improvement, effective communication, and comprehensive training helps prevent accidents and incidents, enhances decision-making, and fosters a safety-first culture within the aviation industry.
By learning from these incidents and embracing SMS, airlines and aviation organizations can continually improve safety and protect passengers and crew.
"Safety Management Systems (SMS) are the wings that carry aviation to new heights of safety and excellence."
Consequences of Lack of SMS Training

When a crew is not trained well in Safety Management Systems (SMS), several negative consequences can arise, potentially compromising aviation safety and operational efficiency. Some of the key issues that may arise due to inadequate SMS training include:
- Increased Safety Risks: Without proper SMS training, crew members may not be equipped to identify and address potential safety hazards effectively. This can lead to an increased likelihood of safety incidents or accidents during flight operations.
- Ineffective Risk Management: SMS emphasizes proactive risk management, where potential risks are identified and mitigated before they escalate. Crew members who lack SMS training may not be able to assess risks adequately or implement appropriate risk controls.
- Poor Decision Making: SMS training helps in developing a systematic approach to decision-making, considering safety factors and potential consequences. A crew that is not well-trained in SMS may make suboptimal decisions during critical situations, which can have serious implications for flight safety.
- Inadequate Emergency Response: During emergencies or abnormal situations, crew members need to act swiftly and effectively. Without SMS training, they may struggle to manage the situation, leading to delays in implementing appropriate emergency procedures.
- Underreporting of Safety Events: SMS encourages the reporting of safety-related events, incidents, and near-misses to facilitate continuous improvement. If the crew is not well-versed in SMS principles, they may be less likely to report safety events, depriving the airline of valuable data for safety analysis.
- Lack of Safety Culture: A strong safety culture is crucial in aviation to foster a proactive safety mindset among all employees. Inadequate SMS training can contribute to a weak safety culture, where safety may not be prioritized or embraced by the crew.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Many aviation authorities require airlines to have an SMS in place and ensure that their employees, including the crew, are adequately trained in SMS implementation. Inadequate SMS training can lead to non-compliance with these regulations, resulting in potential penalties or loss of operating certifications for the airline.
- Reduced Operational Efficiency: Safety and operational efficiency go hand in hand. A crew that lacks proper SMS training may face challenges in implementing safety-related procedures, leading to inefficiencies in operations.
The importance of well-trained crew in Safety Management Systems cannot be overstated. SMS training equips crew members with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage safety risks, make informed decisions, and respond effectively to emergencies.
By investing in comprehensive SMS training, airlines can enhance safety, maintain regulatory compliance, and foster a strong safety culture within their organizations.
“To most people, the sky is the limit. To those who love aviation, the sky is home.”
Jerry Crawford
In the end we just want to emphaise again the Safety Management System (SMS) is a crucial framework that has revolutionized aviation safety practices. By adopting a proactive approach to risk management, SMS empowers aviation organizations to identify and mitigate potential hazards before they escalate into safety incidents or accidents. With its emphasis on continuous improvement and a safety-oriented culture, SMS fosters an environment where safety is prioritized at every level of the organization.
The implementation of SMS has led to tangible benefits in the aviation industry, such as a reduction in accidents, improved decision-making processes, and enhanced communication among stakeholders. Moreover, SMS serves as a solid foundation for compliance with regulatory requirements, instilling confidence in passengers and industry stakeholders.
As aviation continues to evolve and face new challenges, the significance of SMS remains paramount. Embracing SMS principles and investing in comprehensive training for all personnel, including cabin crew and pilots, ensures that safety remains at the forefront of every flight operation.
Ultimately, SMS is more than just a system; it is a philosophy that guides aviation towards safer skies and continuous improvement. By leveraging the principles of SMS, the aviation industry can confidently embark on a journey of safer and more efficient operations, securing a brighter and safer future for all those who take to the skies.
We hope you truly enjoyed reading this blog on AviationX. We have compiled websites and readily available reference materials sourced from the internet, which will help you understand SMS better. Do subscribe to our blog for more such content, which will aid you in mastering All things Aviation! (our tagline)
Some Useful Website Links
Few Videos We Liked On YouTube
Some Flip-books From Useful Websites on SMS
Disclaimer: The flipbooks shared below have been converted from directly downloadable PDFs from different sources without altering any content. For more information and queries regarding the content of the same, you can directly contact the respective websites and sources, as most of them provide all the contact information. Our purpose is merely to assist our readers in obtaining a single, comprehensive overview of all relevant content on the topic after reading the blog.